

Consequently, these monitoring tools can generate alerts or shut down ports when you use wake-up proxy.ĭo not use wake-up proxy if your network monitoring tools and services do not allow MAC flaps. Some network monitoring tools look for this behavior and can assume that something is wrong. However, this behavior is known as a MAC flap and is unusual for standard network operation. Wake-up proxy works by informing the network switch that a different network adapter is using the port that was registered by another network adapter. The manager computer also responds to ARP requests on behalf of the sleeping computer and replies with the MAC address of the sleeping computer.ĭuring this process, the IP-to-MAC mapping for the sleeping computer remains the same. The manager computer also sends ARP packets for the sleeping computers to keep the entry fresh in the ARP cache. This behavior makes the network switch behave as if the sleeping computer has moved to the same port that the manager computer is on. The redirection is achieved by the manager computer broadcasting an Ethernet frame that uses the sleeping computer's MAC address as the source address. Manager computers ask the network switch to redirect network traffic for the sleeping computers to themselves. If this action happens, the remaining guardian computers wake up another computer on the subnet so that the subnet continues to have three guardian computers. Guardian computers honor shutdown or restart commands, for example, as a result of maintenance tasks. This state means that they stay awake, despite any configured power policy to sleep or hibernate after a period of inactivity. To achieve this requirement, three computers are non-deterministically chosen to be guardian computers for the subnet. To support wake-up proxy, at least three computers must be awake for each subnet. Computers that don't respond will no longer be assumed to be asleep and will not be woken up by wake-up proxy.
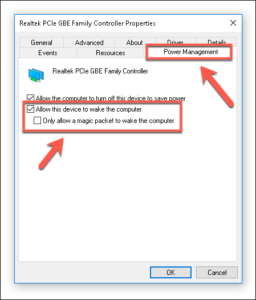
The computers that are awake become manager computer for the subnet.īecause it's possible that a computer might not respond because of a reason other than it's asleep (for example, it's turned off, removed from the network, or the proxy wake-up client setting is no longer applied), the computers are sent a wake-up packet every day at 2 P.M. If there's no response from other computers, they're assumed to be asleep. They do this check by sending each other a TCP/IP ping command every five seconds. When the site is configured for Wake On LAN and clients are configured for wake-up proxy, the process works as follows:Ĭomputers with the Configuration Manager client installed and that aren't asleep on the subnet check whether other computers on the subnet are awake. Wake-up proxy uses a peer-to-peer protocol and elected computers to check whether other computers on the subnet are awake, and to wake them if necessary. You can supplement the traditional wake-up packet method by using the wake-up proxy client settings.
REMOTE WAKE UP OF DESKTOP COMPUTER HOW TO
How to wake up clients in Configuration ManagerĬonfiguration Manager supports traditional wake-up packets to wake up computers in sleep mode when you want to install required software, such as software updates and applications. For more information about how the new version of Wake on LAN functions starting in 1810 and enabling either or both versions, see How to configure Wake on LAN. Both versions of Wake on LAN can, and in many cases will, be enabled simultaneously. This functionality still exists in Configuration Manager version 1810, which also includes a newer version of Wake on LAN too.

This article describes how an older version of Wake on LAN functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
